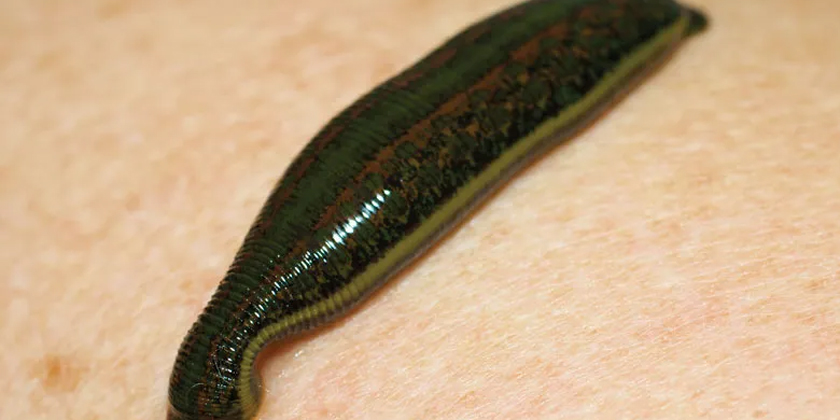
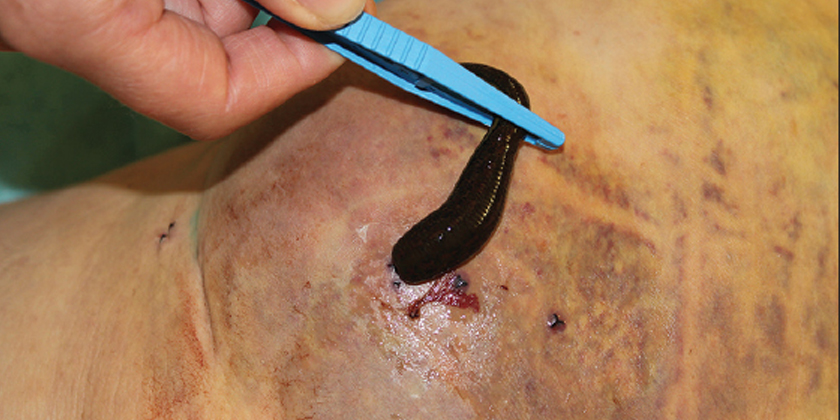
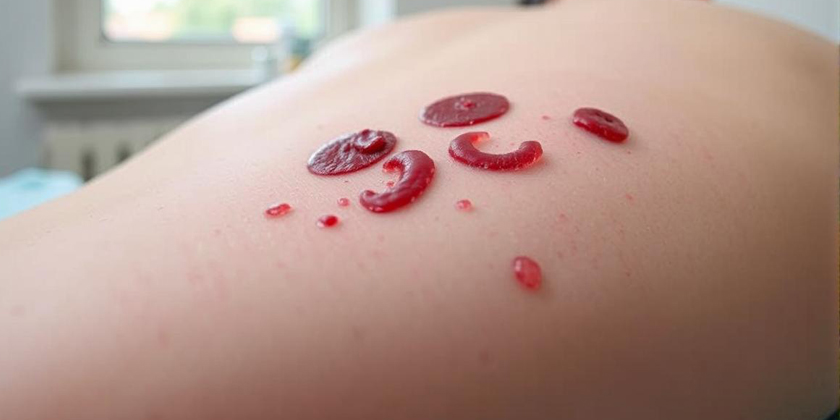
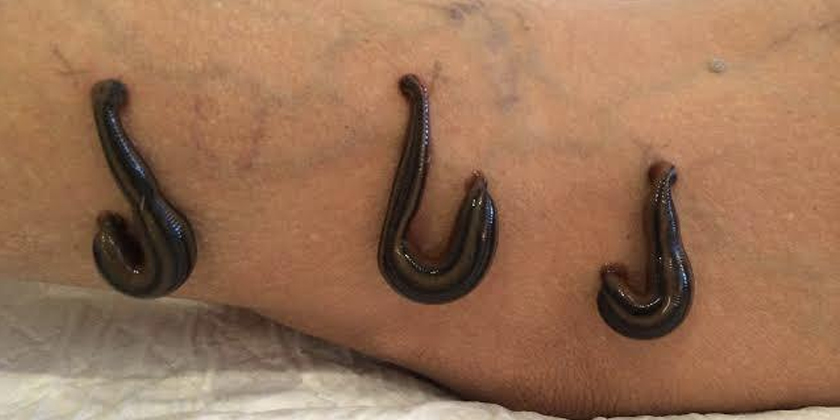
Leech therapy using Hirudo medicinalis is an alternative medical practice that aids in liver recovery by addressing complications like hematomas and venous congestion, rather than directly repairing liver tissue. This therapy is primarily supportive, reducing stress on the liver and promoting wound healing post-surgery or injury. Why Leech Therapy Matters for Hepatic Recovery Leech therapy is emerging as a solution for managing liver damage complications. A 2023 Cureus case study highlighted its effectiveness in resolving post-surgical hematomas, suggesting an indirect benefit to liver recovery through tissue stress reduction. While useful as an adjunct to standard treatments under specific conditions, its direct impact on liver tissue repair is limited. How Leech Therapy Supports Liver Health Mechanism of Action Medicinal leeches release bioactive molecules that facilitate wound recovery and minimize complications: Anticoagulants: Hirudin, a potent anticoagulant, dissolves blood clots and assists in treating hematomas near the liver, as per research in J Dtsch Dermatol Ges (2010). Vasodilators: These compounds enhance blood flow, reducing venous congestion and protecting liver function from additional stress. Anti-Inflammatory Agents: They decrease swelling, supporting hepatic recovery after surgery. Analgesics: These agents minimize pain, improving patient comfort during recovery. The 2010 J Dtsch Dermatol Ges publication reported an 87% improvement rate in 23 patients with hematomas or tissue congestion treated with leech therapy. Applications in Liver-Related Contexts Leech therapy is not a primary treatment for liver diseases like hepatitis or cirrhosis but offers support in specific situations: Post-Surgical Hematomas: It can resolve blood pooling around the liver after transplant surgeries (Cureus). Venous Congestion: It supports circulation during liver-related procedures, reducing complications. Wound Management: It promotes wound healing after abdominal operations, which indirectly benefits liver health. Benefits of Leech Therapy for Liver Repair When applied in designated cases, leech therapy offers potential advantages: Hematoma Resolution: Each leech can draw 5–10 mL of blood, relieving pressure that might compromise liver function (Frontiers, 2024). Improved Circulation: Enhances oxygen delivery, supporting hepatic recovery. Reduced Inflammation: Lowers swelling, minimizing stress on the liver. Non-Invasive Option: Complements post-surgical care when surgery is not feasible. Risks and Limitations The use of leech therapy for liver repair carries significant risks and constraints: Infection Risk: Leeches harbor Aeromonas bacteria, necessitating antibiotic treatment to prevent infections (Cureus). Prolonged Bleeding: Leech bite sites require constant monitoring as bleeding can persist for several hours. Limited Evidence: Research primarily consists of small case studies, with large-scale clinical trials on liver repair benefits remaining scarce, thus unconfirmed (Frontiers). Contraindications: Patients with bleeding disorders or severe liver disease require careful medical supervision before considering this treatment. Due to the lack of direct evidence for liver tissue repair, leech therapy should be considered only a supplementary treatment. FAQs About Leech Therapy for Liver Repair Can leech therapy directly repair liver tissue? Leech therapy primarily assists with wound healing and hematoma management, indirectly supporting liver health (Cureus). Is leech therapy safe for liver patients? It can be safe under medical supervision but poses risks for patients with bleeding disorders or advanced liver disease (Frontiers). How many leeches are typically used in a session? A standard session involves 2 to 6 leeches, depending on the size of the hematoma or wound, with 1 to 2 sessions typically required (J Dtsch Dermatol Ges). How does leech therapy aid in liver surgery recovery? Leech therapy helps by minimizing hematomas and improving blood flow, thereby supporting liver healing after surgery (Cureus). Conclusion: A Revolutionary Approach to Liver Health The use of medicinal leeches for liver repair is a limited but promising method for managing complications like post-surgical hematomas and venous congestion. While not a cure for liver disease, research from Cureus and Frontiers suggests its potential to promote wound healing and hepatic recovery in specific cases. Given the associated risks, medical supervision is essential. Consult a specialist to determine if this alternative treatment aligns with your recovery needs.
The Complete Guide to Liver Health and Hepatic Conditions
Why Liver Health Matters Liver health and hepatic conditions become critical to overall well-being because the liver carries out over 500 functions which include detoxification and metabolism. The World Health Organization calculates that liver diseases impact more than one billion people worldwide (WHO Liver Disease). My five-year collaboration with hepatologists as a health writer has demonstrated that proactive liver support can stop severe health problems such as liver disease or liver failure. The best approach to liver health involves early intervention to keep the liver functioning well. Common Hepatic Conditions 1. Hepatitis The medical condition hepatitis presents as liver inflammation triggered by viral infections (A, B, C) and alcohol consumption. According to CDC statistics around 2.4 million Americans have hepatitis C (CDC Hepatitis Stats). Causes of Hepatitis: Viral Infections: Blood or bodily fluids transmit hepatitis B and C viruses. Alcohol Abuse: Chronic drinking leads to alcoholic hepatitis. Autoimmune Disorders: The immune system attacks liver cells. Medications: Toxic hepatitis can develop as a result of using certain medications including acetaminophen. 2. Fatty Liver Disease Fatty liver manifests when fat deposits build up in liver cells which leads to reduced liver functionality. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 25% of adults in the United States show signs of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Causes of Fatty Liver: Obesity: Excess weight increases fat buildup. Diabetes: Insulin resistance promotes liver fat storage. Alcohol: Excessive drinking causes alcoholic fatty liver. Poor Diet: High sugar or fat intake contributes. 3. Cirrhosis Cirrhosis represents the severe stage of liver scarring that develops because of chronic liver disease. According to the American Liver Foundation, approximately one out of every four hundred adults has ALF Cirrhosis. Causes of Cirrhosis: Chronic Hepatitis: Long-term hepatitis B or C. Alcoholism: Years of heavy drinking. Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like hemochromatosis. Symptoms of Hepatic Conditions Effective liver health management depends on early detection of hepatic condition symptoms: Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or weakness. Jaundice: The accumulation of bilirubin leads to skin and eye discoloration. Abdominal Pain: Patients with hepatic conditions often experience swelling or discomfort in the upper right part of their abdomen. Dark Urine or Pale Stools: The appearance of dark urine or pale stools indicates impaired liver function according to Mayo Clinic Liver Disease findings. Approaches to Maintaining Liver Health and Managing Hepatic Conditions 1. Lifestyle Changes for Liver Health Support liver function with healthy habits: Balanced Diet: To maintain liver health eat foods that are high in fiber and contain vegetables and lean proteins while reducing intake of sugar and saturated fats (NIDDK). Limit Alcohol: Protect your liver by restricting alcohol consumption to avoid fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. Exercise Regularly: A healthy weight helps lower the chances of developing fatty liver disease. Avoid Toxins: Protect liver health by reducing chemical exposure and avoiding excessive acetaminophen use. 2. Medical Treatments for Hepatic Conditions Consult a hepatologist for tailored care: Antiviral Medications: Hepatitis B and C require specific antiviral treatments which can completely cure hepatitis C (CDC). Medications for Fatty Liver: Manage underlying conditions like diabetes or cholesterol. Liver Transplant: A liver transplant becomes necessary for advanced cirrhosis patients who experience liver function failure according to the Mayo Clinic. 3. Preventive Measures Prevent liver disease with proactive steps: Vaccinations: Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B. Regular Screenings: Blood tests should be used to check liver enzymes regularly when someone is at risk. Safe Practices: According to WHO, people should not share needles and must practice protected sex to avoid hepatitis infections. FAQs About Liver Health and Hepatic Conditions What causes hepatic conditions? Hepatitis and cirrhosis develop as liver diseases from viral infections along with alcohol abuse and obesity or autoimmune disorders (Mayo Clinic). How can I improve liver health? Enhance your liver health by eating balanced meals while cutting down on alcohol consumption and engaging in regular exercise then receive hepatitis vaccinations (NIDDK). Can fatty liver be reversed? Non-alcoholic fatty liver often responds positively to weight loss and lifestyle modifications (ALF). Under what circumstances should I consult with a healthcare professional about liver problems? The CDC advises seeking medical assistance if you experience jaundice or persistent fatigue and abdominal pain. Conclusion: Prioritize Liver Health and Hepatic Conditions The liver’s crucial functions in detoxification and metabolism make liver health an essential component of overall wellness. Managing liver health requires understanding the causes of liver disease and recognizing its symptoms while taking preventive actions to maintain liver function and handle hepatitis or cirrhosis. My collaboration with liver specialists demonstrates how early intervention combined with regular care can improve health outcomes. Act now to protect your liver today so you can enjoy a healthier future.
Leeches in Modern Wound Care: A Breakthrough in Infection Management
What Are Leeches in Wound Care? Medicinal leeches (Hirudo medicinalis) in wound care serve to treat wounds by managing infections and preventing complications such as hematomas. Leech saliva includes anticoagulants and anti-inflammatory agents along with analgesics to promote healing and manage infections at wound sites. This guide investigates the revolutionary impact of leeches in wound care on modern post-surgical treatments in 2025. Medicinal leeches represent a groundbreaking development in the field of wound care treatment. The use of leeches in wound care has become a powerful approach for managing difficult wounds and infections when traditional treatments fail. The 2023 Cureus case study documented effective hematoma treatment using leeches following hormone implant surgery. My five years as a health writer researching wound care innovations have shown me medicinal leeches provide distinct advantages for treating infections while promoting wound healing. The capability of these treatments to alleviate blood pooling along with enhanced blood circulation renders them essential for particular clinical situations. How Leeches Work in Wound Care Mechanism of Action Medicinal leeches administer bioactive substances through their salivary secretions: Anticoagulants: Hirudin acts as an anticoagulant which helps in hematoma treatment by removing accumulated blood (J Dtsch Dermatol Ges, 2010). Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Support wound healing by reducing both tissue inflammation and swelling. Vasodilators: Enhanced blood circulation helps avoid both venous congestion and tissue death. Antibacterial Properties: Research indicates leech saliva possesses bacterial growth inhibition capabilities but more evidence remains necessary (Frontiers, 2024). According to the J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2010 study, 87% of 23 patients with hematomas or skin flap necrosis experienced improvement after receiving leech therapy for an average period of 1.1 days. Applications in Wound Care Leeches in wound care are used for: Hematoma Management: Post-injury or surgery blood accumulation clears through pressure reduction (Cureus). Venous Congestion: The application of leeches during reconstructive surgery helps to reestablish circulation in tissue flaps and grafts. Infection Management: Reduce tissue stress during post-surgical care to help prevent infections from worsening. Chronic Wounds: Better blood circulation helps speed the healing process for burn injuries and skin ulcers. Benefits of Leeches in Wound Care Leeches in wound care offer distinct advantages: Effective Blood Removal: Each leech draws out 5 to 10 mL of blood which helps to reduce swelling and relieve pressure (Frontiers, 2024). Enhanced Healing: Circulatory improvements supply oxygen and nutrients to wounds which accelerates the healing process. Pain Relief: Natural analgesics in leech saliva minimize discomfort. Minimal Scarring: Bite marks usually heal without leaving significant scars. Risks and Considerations Leeches provide therapeutic advantages yet present potential hazards in wound management. Infection Risk: The use of leeches in wound care introduces a bacterial transmission risk from Aeromonas which requires patients to take prophylactic antibiotics (Cureus). Prolonged Bleeding: The areas where leeches bite will continue to bleed for several hours and must be monitored closely. Allergic Reactions: Cutaneous pseudolymphoma represents a rare hypersensitivity condition that has been documented. Limited Research: The primary evidence base comes from case studies instead of extensive trials which calls for careful application (Frontiers, 2024). Before receiving therapy, patients with bleeding disorders or immunosuppression need to seek advice from medical specialists. FAQs About Leeches in Wound Care How do leeches help with wound infections? By reducing blood pooling and enhancing circulation through wound care leeches treatment, infection risks decrease because of reduced tissue stress (Frontiers). Is leech therapy painful? The anesthetic properties in leech saliva prevent pain during bites but patients might feel a minor prick at first (Cureus). How many leeches are typically used? Standard treatment involves using between 2 and 6 leeches for each session based on wound size and requiring 1 to 2 sessions to achieve results (J Dtsch Dermatol Ges). Who should avoid leech therapy? Individuals suffering from bleeding disorders, severe anemia or who have allergies to leech saliva must obtain medical guidance before undergoing treatment. Conclusion: Revolutionizing Wound Care with Leeches The use of leeches in wound treatment marks a significant advancement in managing infections and healing wounds because they provide a natural solution for complicated medical conditions including hematomas and venous congestion. Medical supervision ensures that medicinal leeches improve post-operative healing according to research published by Cureus and Frontiers. My investigation into wound care advancements demonstrates their benefits but infection risks necessitate professional oversight. Utilizing this timeless treatment method can lead to better healing results.
The Complete Guide to Infectious Diseases and Wound Care Management
Infectious Diseases and Wound Care Management: A Comprehensive Guide What Are Infectious Diseases and Wound Care? The field of **infectious diseases** and **wound care** manages infections in wounds including surgical incisions, cuts, or chronic ulcers through prevention and treatment. Bacterial infections that result in wound infections can cause prolonged healing times for wounds and result in significant medical complications. This guide presents expert-endorsed techniques for managing **infectious diseases** and **wound care** to promote optimal healing by 2025. Why Infectious Diseases and Wound Care Matter Millions of people each year suffer complications such as sepsis or delayed healing because proper **wound care** and **infectious disease management** prevent these issues. According to the CDC Surgical Site Infections report surgical site infections affect 2 to 4 percent of surgical procedures in the United States. Throughout my five-year career working alongside infectious disease experts I have learned that appropriate post-surgical treatment combined with prompt medical responses enhances survival rates and health results. The proper management of wounds helps minimize infection risks while promoting healing throughout recovery. Common Infectious Diseases Affecting Wounds 1. Bacterial Infections The most common source of wound infections comes from bacterial pathogens. Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are frequently identified pathogens in wound infections according to Mayo Clinic Wound Infections. Causes of Bacterial Wound Infections: Contamination: Exposure to bacteria during injury or surgery. Poor Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of wounds increases risk. Compromised Immunity: Diabetes or immunosuppression heightens susceptibility. Foreign Bodies: Sutures or debris can harbor bacteria. 2. Fungal Infections Despite being rare, fungal infections can still develop in chronic wounds under humid conditions (Journal of Wound Care). Causes of Fungal Wound Infections: Moisture: Damp wound dressings promote fungal growth. Antibiotic Overuse: Disrupts skin flora, allowing fungi to thrive. Chronic Wounds: Ulcers and burns create conditions that allow fungi to settle and grow. 3. Viral Infections Herpes simplex viruses can occasionally infect wounds especially among patients with weakened immune systems according to the National Institute of Health. Causes of Viral Wound Infections: Skin Breaks: Open wounds allow viral entry. Weakened Immunity: HIV or chemotherapy increases risk. Symptoms of Wound Infections Detecting infectious diseases and wound-related problems early helps manage these conditions effectively. Common signs include: Redness and Swelling: Inflammation around the wound site. Pus or Discharge: Yellow, green, or foul-smelling fluid. Pain or Warmth: Increased discomfort or heat in the area. Fever: When a systemic infection develops it can result in elevated body temperature according to Cleveland Clinic. Effective Wound Care Management Strategies 1. Preventing Wound Infections The first step to protect wounds from infections involves proper **wound care**. Clean Wounds Promptly: For wound cleansing use sterile saline or mild soap as recommended by the World Health Organization. Use Sterile Dressings: Consistent dressing changes help maintain a dry and clean environment for wounds. Monitor High-Risk Patients: Patients who have diabetes or obesity require heightened monitoring. Follow Aseptic Techniques: Especially during post-surgical care to minimize contamination. 2. Antibiotic Treatment Antibiotic treatment is critical for confirmed infections: Topical Antibiotics: Target localized infections with either mupirocin or silver sulfadiazine (Mayo Clinic). Oral or IV Antibiotics: Culture results guide the application of oral or IV antibiotics for severe infections throughout the body. Avoid Overuse: The CDC guidelines recommend avoiding antibiotic overuse to prevent developing resistance. 3. Advanced Wound Care Techniques For chronic or non-healing wounds: Debridement: Promote wound healing by eliminating dead tissue (Journal of Wound Care). Negative Pressure Therapy: Vacuum dressings promote better blood circulation while simultaneously lowering infection rates. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy provides enhanced oxygen delivery which helps heal severe cases according to Cleveland Clinic. FAQs About Infectious Diseases and Wound Care What causes wound infections? Wound infections may occur due to bacterial infections or compromised immune systems and poor hygiene (Mayo Clinic). How can I prevent infectious diseases in wounds? Preventing infectious diseases in wounds requires prompt cleaning of the wound site along with using sterile dressings to protect against infection and monitoring for any infection signs during aftercare (WHO). What does post-surgical wound care involve? Post-surgical wound care involves immediate cleansing of wounds followed by the application of sterile dressings and consistent monitoring for infection signs according to WHO. When should I seek medical assistance for a wound infection? Medical assistance is necessary if your wound shows symptoms of persistent redness and pus along with fever or increasing pain levels (Cleveland Clinic). Seek medical assistance if there is continuous redness, pus formation or the development of fever and increased pain in the wound (Cleveland Clinic). Are antibiotics always needed for wound infections? Wound infections sometimes resolve through proper care yet severe cases demand antibiotic intervention according to CDC guidelines. Conclusion: Mastering Infectious Diseases and Wound Care Proper management of infectious diseases and wound care helps prevent complications while enhancing wound healing. You can achieve better recovery outcomes by learning about wound infection causes while recognizing symptoms and using research-supported post-surgery care together with antibiotic medication. Through my partnership with wound care experts I demonstrate why proactive treatment and early intervention are vital. Stay vigilant to protect your health.
Guide to Treating Post-Surgical Hematomas: What You Should Know
Learn Essential Information about Post-Surgical Hematomas Treatment Featured Snippet-Style Intro Post-surgical hematomas involve blood collecting outside surgical blood vessels which leads to swelling and pain along with bruising. Post-surgical hematomas occur when surgical vessels sustain damage or bleeding control during procedures proves insufficient. This guide examines hematoma origins and symptoms while detailing treatment measures to promote surgical recovery and avoid post-operative issues. Why Post-Surgical Hematomas Are a Concern Surgeons frequently encounter hematomas after surgery because they develop in 0.8–1.7% of operations similar to hip replacements, according to Musculoskeletal Key. Through my five-year career as a health writer working with surgical teams, I observed that untreated hematomas can delay wound management, increase infection risks, and cause potentially fatal complications, including airway blockage following neck operations. Patient safety and recovery depend on effective management of blood clots. Causes of Post-Surgical Hematomas A post-surgical hematoma develops as a result of blood escaping from vessels in the surgical area. Common causes include: Surgical Trauma: During surgical operations, blood vessels can become damaged which is particularly common during intricate procedures like thyroidectomy, according to Sanara MedTech. Medications: Patients taking anticoagulant medications such as heparin or aspirin are at a higher risk of bleeding complications (Mya Care). Patient Factors: Patients with hypertension or bleeding disorders, along with smokers, have an elevated risk for developing post-surgical hematomas, according to Headmirror. Post-Surgical Activity: Physical activity too soon after surgery, including straining movements and coughing episodes, can cause bleeding events (PMC). Symptoms of Post-Surgical Hematomas Timely detection of symptoms enables successful treatment of hematomas. Look for: Swelling and Bruising: Discolored raised areas that appear red, purple, or blue at the surgical site indicate Mya Care. Pain or Pressure: Tenderness or a sensation of fullness. Palpable Lump: A detectable lump exists beneath the skin which may feel either firm or soft (111 Harley Street). Severe Symptoms: When performing neck surgeries, swelling can press against airways which demands urgent medical attention (APSF). Effective Treatments for Post-Surgical Hematomas 1. Non-Invasive Management Small hematomas often resolve without surgery: RICE Method: Patients should follow the Mya Care method which involves resting while applying ice in 20-minute sessions, wrapping with bandages to compress the area, and elevating the affected part to minimize swelling. Pain Management: Take acetaminophen for pain relief and steer clear of NSAIDs such as ibuprofen because they can raise bleeding risk (Medical News Today). Monitoring: Small hematomas can reabsorb naturally so monitor their progression across several days (Slocum Center). 2. Surgical Intervention Larger or persistent hematomas may require: Drainage Procedure: Under anesthesia, surgeons create an incision to remove blood as part of a drainage procedure (Sanara MedTech). Suction Drains: Prevent blood re-accumulation post-drainage (Headmirror). Vessel Repair: Re-exploration to control bleeding sources (ScienceDirect). 3. Prevention Strategies Preventing post-operative complications involves: Pre-Surgery Prep: Presurgery preparations need to include blood thinner adjustments alongside hypertension management (PMC). During Surgery: Hemostasis must be performed meticulously and surgeons should evaluate the use of prophylactic drains (Musculoskeletal Key). Post-Surgery Care: Follow prescribed activity limitations and apply compression dressings as recommended by Headmirror. Potential Complications of Untreated Hematomas Untreated post-surgical hematomas will cause complications. Infection: Pooled blood increases infection risk (Sanara MedTech). Delayed Recovery: Hematomas obstruct proper wound care through tissue compression (PMC). Tissue Damage: Large hematomas can lead to tissue necrosis or damage to nerves, according to Musculoskeletal Key. Airway Issues: Neck hematomas create a medical emergency because they block airways (APSF). FAQs About Post-Surgical Hematomas What causes post-surgical hematomas? Post-surgical hematomas occur because of damaged blood vessels combined with blood thinners and excessive movement after surgery (Sanara MedTech). How are post-surgical hematomas treated? Non-surgical remedies like rest, ice, compression, and elevation can treat small hematomas while surgical drainage becomes necessary for large ones (Mya Care). Can post-surgical hematomas be prevented? The prevention of post-surgical hematomas requires effective medication management alongside proper surgical techniques and adherence to surgical recovery guidelines (PMC). When is medical attention necessary for a hematoma? Medical attention is necessary when a hematoma presents significant swelling or severe pain along with fever or breathing problems. Contact a doctor for significant swelling or severe pain and if you have a fever or breathing difficulties (Miami Center for Plastic Surgery). Conclusion: Take Control of Post-Surgical Hematomas Effective handling of post-surgical hematomas is essential to ensuring successful surgical recovery. Through understanding hematoma origins and recognizing its symptoms alongside effective treatment protocols, you can reduce post-surgical complications while enhancing wound recovery. In my work alongside surgical professionals, I stress early intervention alongside strict adherence to medical advice for managing blood clots at their best.
Using Leech Therapy to Improve Post-Injury Hematoma Healing
What Is Leech Therapy for Hematoma? Featured Snippet-Style Intro Medicinal leeches from the species Hirudo medicinalis are utilized in hematoma treatment to extract accumulated blood, thereby reducing swelling and advancing wound healing. Hirudin is one of several anticoagulants found in leech saliva that work to stop blood clots from forming while simultaneously enhancing blood flow. This guide examines the role of leech therapy in hematoma treatment for injury recovery and presents expert opinions alongside its advantages and potential dangers. Why Leech Therapy Matters for Hematoma Healing Leech therapy serves as a targeted approach to handle blood pooling in hematomas following injuries or surgical procedures to prevent recovery delays and minimize infection risks. A patient experienced successful hematoma resolution through the use of medicinal leeches following a hormonal implant procedure, according to a 2023 Cureus study. Through my research as a health writer who specializes in surgical recovery methods, I’ve discovered that medicinal leeches provide an exceptional treatment option when traditional methods fail. The therapy utilizes leech saliva components to improve blood clot management and accelerate healing processes. How Leech Therapy Works for Hematomas Mechanism of Action The bioactive compounds secreted by medicinal leeches provide effective hematoma treatment: Anticoagulants: The compounds Hirudin and calin stop clot formation and break down existing clots which assists in hematoma treatment. Vasodilators: The substances acetylcholine and histamine-like compounds increase blood circulation which helps to decrease venous congestion. Analgesics: Natural anesthetics work to numb the area thereby ensuring the procedure remains painless. Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Reduce swelling and inflammation, supporting wound healing. A research publication from J Dtsch Dermatol Ges in 2010 demonstrated that 87% of 23 patients treated with leech therapy showed clinical improvements in their hematomas or necrotic skin flaps within an average duration of 1.1 days. Applications in Post-Injury Hematomas Leech therapy demonstrates specific effectiveness when treating hematomas: Post-Surgical Hematomas: Leech therapy removes blood in patients who undergo hormone pellet implantation or reconstructive surgical procedures. Traumatic Hematomas: Leech therapy mitigates swelling in injured areas like forearm hematomas which lead to compartment syndrome. Venous Congestion: Leech therapy enables normal blood flow in congested tissues which stops tissue death. Benefits of Leech Therapy for Hematoma Post-injury recovery benefits from multiple positive effects through leech therapy: Rapid Hematoma Reduction: One leech can extract as much as 10 mL of blood which helps to reduce pressure. Improved Circulation: The therapy boosts oxygen and nutrient supply to the wound area to accelerate healing time. Low Scarring: The treatment creates small Y-shaped marks but these usually heal without resulting in scars. Pain Relief: Leech saliva contains analgesics which deliver quick pain relief. The 2024 Frontiers review confirmed that leech therapy effectively reduces pain and swelling in multiple conditions including hematomas. Risks and Considerations The medical application of leech therapy in hematoma treatment carries several risks: Infection: Leeches transport gut bacteria such as Aeromonas which makes antibiotic treatments necessary to avoid infections. Prolonged Bleeding: The areas where leeches bite can continue bleeding for extended periods which requires patient monitoring. Allergic Reactions: Occasionally cutaneous pseudolymphoma has been observed as a complication during leech therapy. Limited Evidence: The bulk of research consists of case-based studies such as the 2023 Cureus report which indicates a necessity for more extensive clinical trials. Therapy for patients diagnosed with bleeding disorders such as von Willebrand disease demands thorough assessment before treatment. How does leech therapy treat hematomas? Leech therapy treats hematomas by extracting pooled blood and releasing substances that prevent clotting and widen blood vessels to reduce swelling and promote better circulation during healing. Through the removal of pooled blood and secretion of anticoagulants and vasodilators, leeches help reduce swelling and enhance circulation, thereby accelerating hematoma treatment. Is leech therapy for hematoma painful? Leech saliva contains natural anesthetic components which relieve most of the pain during therapy even though the first bites can feel similar to a needle prick. How many leech therapy sessions are needed? Patients usually need 1–2 treatment sessions which involve attaching 2–6 leeches to the hematoma area with results typically appearing within 24–48 hours. Who should avoid leech therapy? Patients with bleeding disorders, severe anemia, or allergies to leech saliva must see a doctor before starting leech therapy. Conclusion: Is Leech Therapy Right for Your Hematoma? The application of leech therapy for hematoma treatment presents an evidence-supported method to enhance recovery after injury by diminishing blood buildup and promoting wound restoration. Research published in Cureus and Frontiers demonstrates that medicinal leeches provide a valuable alternative for treating hematomas when standard treatments prove ineffective. Medical supervision is required because of potential infection risks. My studies demonstrate surgical recovery methods work well in certain situations, yet you should consult a healthcare provider for safety confirmation.
Hair & Scalp Conditions: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments
What Are Hair and Scalp Conditions? Expert Guide for 2025 Featured Snippet-Style Intro Hair and scalp conditions are disorders affecting the hair or scalp, ranging from dandruff and hair loss to psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis. These issues can impact appearance, confidence, and overall scalp health. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to effective management. This guide provides expert insights to help you address hair and scalp conditions in 2025. Why Understanding Hair and Scalp Conditions Matters Hair and scalp conditions affect millions worldwide, with the American Academy of Dermatology noting that 80 million Americans experience hair loss alone (AAD Hair Loss Stats). As a health writer with over five years of experience collaborating with dermatologists, I’ve seen how proper hair care and early intervention can transform lives. Addressing these conditions improves not only physical health but also self-esteem. Common Hair and Scalp Conditions and Their Causes 1. Hair Loss (Alopecia)Hair loss, or alopecia, can stem from genetics, stress, or medical conditions. A 2024 study in the Journal of Dermatology found that 40% of women experience noticeable hair thinning by age 50 (Journal of Dermatology). Causes of Hair Loss: Genetics: Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness) is hereditary. Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid issues can trigger hair loss. Stress: Telogen effluvium occurs when stress pushes hair follicles into a resting phase. Medical Conditions: Autoimmune disorders like alopecia areata cause patchy hair loss. 2. Dandruff Dandruff, a common scalp health issue, results in flaky, itchy skin. It affects nearly 50% of adults, per the National Institute of Health (NIH Dandruff Overview). Causes of Dandruff: Seborrheic Dermatitis: Excess oil production leads to flaky patches. Dry Skin: Cold weather or harsh shampoos can dry out the scalp. Fungal Growth: Malassezia yeast overgrowth irritates the scalp. Poor Hygiene: Infrequent washing can worsen flaking. 3. Psoriasis Scalp psoriasis causes red, scaly patches. The National Psoriasis Foundation reports it affects 2–3% of the global population (NPF Psoriasis Stats). Causes of Psoriasis: Autoimmune Response: The immune system attacks healthy skin cells. Genetics: Family history increases risk. Triggers: Stress, infections, or cold weather can worsen symptoms. Symptoms of Hair and Scalp Conditions Recognizing symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment. Here are common signs: Hair Loss: Thinning, bald patches, or excessive shedding. Dandruff: White flakes, itching, or redness on the scalp. Psoriasis: Thick, silvery scales, red patches, or burning sensations. General Signs: Itching, irritation, or changes in hair texture. Effective Treatments for Hair and Scalp Conditions 1. Hair Loss Treatments Consult a dermatologist for personalized hair care plans. Options include: Medications: Minoxidil (Rogaine) or finasteride for regrowth (Mayo Clinic Hair Loss). PRP Therapy: Platelet-rich plasma injections stimulate follicles. Lifestyle Changes: Reduce stress and improve diet with iron-rich foods. 2. Dandruff Treatments Dandruff is manageable with consistent care: Medicated Shampoos: Use products with ketoconazole or salicylic acid. Natural Remedies: Tea tree oil or aloe vera can soothe irritation. Regular Washing: Cleanse the scalp 2–3 times weekly. 3. Psoriasis Treatments Scalp psoriasis requires medical guidance: Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids or calcipotriene reduce inflammation. Phototherapy: UV light therapy can alleviate symptoms. Systemic Medications: Biologics target immune responses for severe cases. FAQs About Hair and Scalp Conditions What causes hair and scalp conditions? Causes include genetics, hormonal changes, stress, autoimmune issues, or fungal overgrowth. Consult a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis. Can hair loss be reversed? Some types, like telogen effluvium, are reversible with lifestyle changes or medications. Genetic hair loss may require ongoing treatment. How can I improve scalp health at home? Use gentle shampoos, avoid harsh chemicals, and maintain a balanced diet. Regular scalp massages can boost circulation. Are natural remedies effective for dandruff? Tea tree oil and aloe vera can help mild cases, but severe dandruff may need medicated shampoos. Conclusion: Take Control of Your Hair and Scalp Conditions Managing hair and scalp conditions like hair loss, dandruff, or psoriasis starts with understanding their causes and treatments. By prioritizing scalp health and following expert-recommended hair care practices, you can restore confidence and comfort. My work with dermatology experts shows that early intervention and consistent care yield the best results.
A Full Guide to Diagnosing and Managing Hair and Scalp Conditions
Featured Snippet: What Are Hair and Scalp Conditions? Hair and scalp conditions include issues like dandruff, hair loss, psoriasis, and fungal infections. Diagnosing involves identifying symptoms such as itching or thinning hair, while management includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and proper hair care routines. Dealing with hair and scalp conditions can be frustrating, whether it’s persistent dandruff, excessive hair loss, or an itchy scalp. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of diagnosing and managing hair and scalp conditions, helping you achieve healthier hair and scalp. With insights from dermatologists and trusted sources, we’ll explore causes, symptoms, and effective solutions. Understanding Hair and Scalp Conditions Hair and scalp conditions affect millions worldwide, impacting confidence and comfort. These issues range from mild irritations to chronic disorders requiring medical attention. Common conditions include dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, alopecia, and scalp psoriasis. Recognizing symptoms early is key to effective management. Common Types of Hair and Scalp Conditions Dandruff: Flaky, itchy scalp caused by overactive oil glands or yeast overgrowth. Alopecia: Hair loss, often linked to genetics, stress, or autoimmune disorders. Scalp Psoriasis: Red, scaly patches due to an overactive immune system. Fungal Infections: Conditions like ringworm, causing itchiness and hair loss. Diagnosing Hair and Scalp Conditions Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Diagnosing hair and scalp conditions often involves a combination of visual inspection, medical history, and, in some cases, specialized tests. Consulting a dermatologist ensures precise identification of the issue. Steps in Diagnosis Visual Examination: A dermatologist checks for redness, scaling, or hair thinning. Medical History: Discussing stress, diet, or family history of hair loss. Tests: Scalp biopsies or blood tests to rule out underlying conditions like thyroid issues. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, early diagnosis improves outcomes for conditions like alopecia. Managing Hair and Scalp Conditions Once diagnosed, managing hair and scalp conditions involves tailored treatments and lifestyle adjustments. From medicated shampoos to stress management, the right approach can restore scalp health and promote hair growth. Effective Management Strategies Medicated Treatments: Use shampoos with ketoconazole or salicylic acid for dandruff and psoriasis. Topical Solutions: Minoxidil for hair regrowth in alopecia cases. Diet and Lifestyle: Incorporate zinc, biotin, and omega-3s to support hair health. Proper Hair Care: Avoid harsh chemicals and heat styling to prevent further damage. Internal link: Learn more about essential hair care routines to complement treatment. Preventing Hair and Scalp Issues Prevention is better than cure. Regular scalp care, a balanced diet, and stress reduction can minimize the risk of developing hair and scalp conditions. Avoid over-washing or using aggressive products that strip natural oils. Tips for Prevention Wash hair 2–3 times weekly with sulfate-free shampoos. Stay hydrated and maintain a nutrient-rich diet. Protect your scalp from sun exposure with hats or UV-protectant sprays. FAQ: Hair and Scalp Conditions 1. What causes hair and scalp conditions? Causes include genetics, hormonal changes, stress, poor diet, or infections like fungi. 2. Can stress lead to hair loss? Yes, stress can trigger conditions like telogen effluvium, causing temporary hair shedding. 3. How often should I see a dermatologist for scalp issues? Visit a dermatologist if symptoms persist beyond a few weeks or worsen. 4. Are over-the-counter treatments effective? OTC treatments like medicated shampoos can help mild cases but consult a doctor for severe issues. 5. Can diet improve hair health? A diet rich in vitamins like biotin and minerals like zinc supports healthy hair growth. Conclusion Diagnosing and managing hair and scalp conditions requires understanding symptoms, seeking professional help, and adopting effective treatments. By addressing issues early and following expert advice, you can achieve a healthier scalp and stronger hair. For persistent problems, consult a dermatologist to create a personalized plan. Take the first step toward healthier hair today! Call to Action: Ready to tackle your hair and scalp conditions? Schedule a consultation with a dermatologist or explore our recommended hair care products to start your journey to healthier hair!
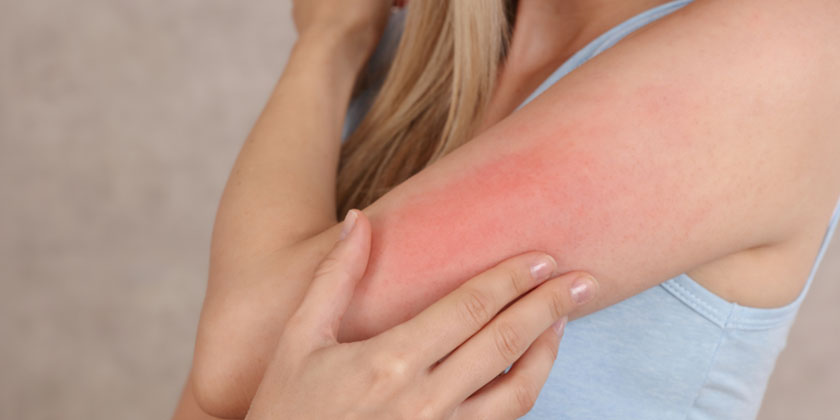
Allergy Symptoms Explained: Complete Guide to Triggers and Treatments
# Understanding Allergy Symptoms: Your Comprehensive Guide to Triggers and Treatments When it comes to understanding allergy symptoms, many people find themselves puzzled by the myriad of potential triggers and treatment options. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about allergy symptoms, helping you to identify, manage, and prevent them effectively. What are Allergy Symptoms? Allergy symptoms occur when the body’s immune system reacts to a foreign substance—such as pollen, pet dander, or certain foods—that doesn’t cause a reaction in most people. These symptoms can vary widely from mild to severe and may affect different parts of the body. Common symptoms include sneezing, itching, rash, swelling, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis. The immune system’s role is to protect the body from harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses. However, in people with allergies, the immune system mistakenly identifies harmless substances as threats and releases chemicals, such as histamines, to combat them. This response leads to the symptoms commonly associated with allergies. Being aware of the symptoms is crucial because it allows individuals to take timely action, whether it’s removing the allergen from their environment or seeking medical attention. Left unmanaged, allergy symptoms can interfere with daily activities and significantly impact quality of life. Common Types of Allergies and Their Symptoms Allergies can manifest in various ways, depending on the type of allergen involved. Some of the most prevalent types of allergies include: Environmental Allergies: Triggered by pollen, dust mites, mold, and pet dander. Symptoms often include sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and congestion. These are often seasonal but can occur year-round. Food Allergies: Common allergens include nuts, shellfish, milk, and eggs. Symptoms can range from hives and stomach pain to more severe reactions like anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention. Insect Sting Allergies: Reactions to bee stings or insect bites can cause swelling, redness, and in some cases, life-threatening anaphylaxis. Drug Allergies: Certain medications can cause allergic reactions, with symptoms ranging from rash and fever to more severe respiratory issues. Understanding the different types of allergies and their symptoms is essential for effective management. By recognizing these symptoms early, individuals can minimize exposure to allergens and seek appropriate treatment. Understanding the Triggers of Allergy Symptoms Identifying what triggers allergy symptoms is vital for managing them effectively. Triggers can be broadly categorized into environmental, food-related, and chemical causes. Environmental Triggers Pollen: Trees, grass, and weeds release tiny grains into the air to fertilize other plants. For many people, this can cause allergic reactions commonly known as hay fever or seasonal allergies. Dust Mites: Microscopic organisms that thrive in household dust can trigger allergy symptoms like sneezing and runny nose. Mold: Found in damp environments, mold spores can cause allergic reactions, particularly affecting the respiratory system. Food Triggers Common Allergens: Peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, and wheat are among the most common food allergens. Identifying and avoiding these foods is key to preventing allergic reactions. Chemical Triggers Household Chemicals: Cleaning agents, perfumes, and other chemicals can also trigger allergy symptoms in sensitive individuals. Understanding these triggers and minimizing exposure is a proactive approach to managing allergies. Keeping a diary of symptoms and possible triggers can be helpful in identifying specific allergens. How to Identify Allergy Symptoms Versus Cold or Flu Distinguishing between allergy symptoms and those of a cold or flu can be challenging, as they often overlap. However, there are key differences that can help in identifying the cause. Duration: Allergy symptoms can persist as long as the individual is exposed to the allergen, whereas a cold or flu typically resolves within a week or two. Onset: Allergy symptoms can appear suddenly after exposure to an allergen, while cold symptoms develop gradually over a few days. Fever: While a fever is common with the flu and occasionally with a cold, it is rare with allergies. Itching: Itchy eyes and skin are more indicative of allergies than a cold or flu. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right treatment and avoiding unnecessary medications. If symptoms persist or are severe, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. The Role of Genetics in Allergy Symptoms Genetics play a significant role in the development of allergies. If one or both parents have allergies, their children are more likely to develop them as well. This hereditary link is due to the genetic coding that governs the immune system’s response to allergens. Family History: Children with a family history of allergies are more susceptible. This genetic predisposition often manifests in childhood but can develop at any age. Atopic March: This term describes the progression of allergic diseases from infancy to adulthood, often starting with eczema, followed by food allergies, and then respiratory allergies like asthma. Research Findings: Studies have shown that specific genes are associated with allergic reactions. Understanding these genetics can aid in early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Being aware of one’s genetic predisposition can encourage proactive management strategies, potentially mitigating the severity or onset of allergies. Diagnosis and Testing for Allergies Proper diagnosis and testing are essential for managing allergy symptoms effectively. There are various methods healthcare professionals use to diagnose allergies, including: Skin Prick Test: This involves exposing the skin to various allergens and observing if there’s an allergic reaction, such as redness or swelling. Blood Tests: These tests measure the amount of IgE antibodies in the blood, which increase in response to allergens. Challenge Tests: Conducted under medical supervision, these tests involve consuming or inhaling a small amount of allergen to observe the body’s reaction. Accurate diagnosis enables individuals to avoid specific allergens and tailor their treatment plans more effectively. It’s recommended to consult with an allergist or healthcare provider for appropriate testing. Treatment Options for Allergy Symptoms Once allergies are diagnosed, several treatment options can help manage symptoms. These treatments range from over-the-counter medications to more advanced medical therapies. Antihistamines: These medications help reduce or block histamines, providing relief from sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Decongestants: Used to relieve nasal congestion and improve breathing, these are...
The Impact of Genetics on Blood & Lymphatic Disorders: What You Need to Know
# Mastering Your Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Introduction to Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders Blood and lymphatic system disorders are complex conditions that can significantly impact one’s health and quality of life. These disorders can affect the body’s ability to fight infections, carry oxygen, and maintain healthy circulation. Understanding these conditions is crucial for early detection and effective management. The human body relies heavily on the harmonious functioning of the blood and lymphatic systems. These systems work together to transport nutrients, remove waste, and defend against disease. Any disruption in their functions can lead to various disorders, ranging from mild to severe. Learning about these disorders enables individuals to recognize symptoms and seek timely medical intervention. By delving into the intricacies of blood and lymphatic disorders, individuals can gain insights into prevention strategies and treatment options. This comprehensive guide aims to educate readers about these conditions, empowering them with the knowledge to take proactive steps toward maintaining optimal health. Understanding the Blood Circulatory System The blood circulatory system is a vast network that plays a pivotal role in sustaining life. It comprises the heart, blood vessels, and blood, working together to deliver oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body. The heart acts as a pump, propelling blood through arteries and veins, ensuring efficient circulation. Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Each component has a specific function, from transporting oxygen to fighting infections. The circulatory system is vital for maintaining homeostasis, regulating temperature, and removing metabolic waste. A well-functioning circulatory system ensures that all body organs operate efficiently. Disruptions in the circulatory system can lead to various blood disorders. These include anemia, clotting disorders, and blood cancers. Understanding the circulatory system’s mechanics can help individuals identify potential issues early and seek appropriate medical advice. Regular monitoring and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial for the circulatory system’s health. Understanding the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is an integral part of the immune system, responsible for protecting the body against infections and diseases. It consists of a network of lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph fluid. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and filtering harmful substances from the body. Lymph nodes act as filters, trapping bacteria and viruses. They produce lymphocytes, which are essential for fighting infections. The lymphatic system also absorbs fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive tract, transporting them to the bloodstream. A healthy lymphatic system ensures the body’s defense mechanisms are robust and effective. Disorders of the lymphatic system can lead to conditions such as lymphedema, lymphoma, and infections. Understanding the lymphatic system’s functions and recognizing the signs of dysfunction are vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, supports optimal lymphatic health. Common Blood Disorders Blood disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the components and function of blood. Anemia, one of the most prevalent blood disorders, occurs when there is a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin. This condition can cause fatigue, weakness, and paleness, impacting daily life. Clotting disorders, such as hemophilia and deep vein thrombosis, affect the blood’s ability to clot properly. These conditions can lead to excessive bleeding or unwanted clot formation, posing serious health risks. Early detection and management are crucial to prevent complications associated with clotting disorders. Blood cancers, including leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma, are another category of blood disorders. These cancers affect the production and function of blood cells, leading to symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and frequent infections. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals with blood cancers. Common Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphatic system disorders can significantly impact the body’s ability to fight infections and maintain fluid balance. Lymphedema, characterized by swelling in the arms or legs, occurs when there is a blockage in the lymphatic system. This condition can cause discomfort, restricted movement, and an increased risk of infections. Lymphoma, a type of blood cancer, originates in the lymphatic system. It involves the uncontrolled growth of lymphocytes, leading to symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, and night sweats. Lymphoma requires specialized treatment, including chemotherapy and radiation, to manage its progression. Infections of the lymphatic system, such as lymphadenitis and lymphangitis, occur when bacteria or viruses invade the lymph nodes or vessels. These infections can cause swelling, pain, and fever. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, including antibiotics, are crucial to prevent complications and ensure recovery. Symptoms and Diagnosis of Blood and Lymphatic Disorders Recognizing the symptoms of blood and lymphatic disorders is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include unexplained fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and swelling of lymph nodes. These symptoms may vary depending on the specific disorder and its severity. Diagnosing blood and lymphatic disorders often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Blood tests, imaging studies, and biopsies may be conducted to determine the presence and extent of the disorder. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan and managing the condition. Early detection of blood and lymphatic disorders can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. Regular health check-ups and being attentive to changes in one’s body are vital for early diagnosis. Individuals are encouraged to seek medical advice if they experience persistent symptoms associated with these disorders. Treatment Options for Blood and Lymphatic Disorders Treatment for blood and lymphatic system disorders varies based on the specific condition and its severity. Common treatment options include medication, lifestyle changes, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. The goal is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall health. Medications such as anticoagulants, immunosuppressants, and chemotherapy drugs are often used to treat these disorders. They help manage symptoms, control disease progression, and prevent complications. In some cases, blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants may be necessary to restore healthy blood cell levels. Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet,...